SaaS developers building on Ethereum face a unique challenge with proration onchain subscriptions: users expect fair billing for mid-cycle tier changes, yet blockchain’s deterministic nature resists automated off-chain conveniences. Proration calculates charges proportionally to usage time, ensuring customers pay only for what they consume. This approach builds trust in decentralized services, where transparency is paramount. With Ethereum at $2,035.03 after a 24-hour dip of $88.16, deploying cost-effective smart contracts now leverages stable network conditions for saas blockchain subscriptions.
Basic Subscription Escrow Contract in Solidity
This Solidity contract provides a basic implementation for subscription payments using an escrow model. Users deposit ETH upfront into their personal balances. The contract owner—typically automated by your SaaS backend or a relayer—manually triggers payments once per billing period (30 days). This setup ensures funds are escrowed securely on-chain before release.
```solidity
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity ^0.8.20;
contract BasicSubscriptionEscrow {
address public immutable owner;
uint256 public immutable subscriptionPrice;
uint256 public constant PERIOD = 30 days;
mapping(address => uint256) public userBalances;
mapping(address => uint256) public lastPaymentTime;
event Deposited(address indexed user, uint256 amount);
event PaymentTriggered(address indexed user, uint256 amount);
constructor(uint256 _subscriptionPrice) {
owner = msg.sender;
subscriptionPrice = _subscriptionPrice;
}
/// @notice Users deposit ETH into their escrow balance
function deposit() external payable {
require(msg.value > 0, "Deposit must be greater than 0");
userBalances[msg.sender] += msg.value;
emit Deposited(msg.sender, msg.value);
}
/// @notice Owner triggers a subscription payment for a user
/// Manual recurring logic: checks time period and balance
function triggerPayment(address user) external {
require(msg.sender == owner, "Only owner can trigger payments");
require(block.timestamp >= lastPaymentTime[user] + PERIOD, "Payment period not elapsed");
require(userBalances[user] >= subscriptionPrice, "Insufficient escrow balance");
userBalances[user] -= subscriptionPrice;
payable(owner).transfer(subscriptionPrice);
lastPaymentTime[user] = block.timestamp;
emit PaymentTriggered(user, subscriptionPrice);
}
/// @notice Owner can withdraw excess contract balance if any
function withdrawExcess() external {
require(msg.sender == owner, "Only owner");
uint256 balance = address(this).balance;
require(balance > 0, "No excess balance");
payable(owner).transfer(balance);
}
/// @notice View function to check if a user can be billed
function canTriggerPayment(address user) external view returns (bool) {
return block.timestamp >= lastPaymentTime[user] + PERIOD &&
userBalances[user] >= subscriptionPrice;
}
}
```**Key components:**
– **Escrow balances**: Prevent overdrafts with per-user tracking.
– **Time-based gating**: `PERIOD` enforces monthly billing cycles.
– **Manual triggers**: `triggerPayment` simulates recurring logic; ideal for testing or custom automation.
– **Safety checks**: Immutables, events, and view functions for transparency.
Extend this for proration by calculating partial payments proportional to time elapsed since `lastPaymentTime[user]`. Use oracles for off-chain automation in production.
Recurring payments on Ethereum demand manual triggers, as confirmed across developer forums. No native automation exists onchain; each renewal requires a transaction. This limitation, highlighted in Ethereum Stack Exchange discussions, shifts reliance to user-initiated actions or external keepers. Yet, it opens doors for precise solidity prorated billing, where contracts enforce rules immutably.
Navigating Recurring Payments Limitations on EVM Chains
Ethereum’s gas-based model prevents perpetual automation. Smart contracts sit dormant until called. For recurring payments ethereum proration, developers must design around this. Common strategies include:
- User-triggered renewals with time-locked access.
- Approval-based pull payments, where users pre-approve contract withdrawals.
- Offchain relayers or Chainlink Automation for scheduled checks.
These methods ensure payments align with cycles, but proration adds complexity. Imagine a monthly subscription at 100 USDC. A user upgrades on day 15 to a 200 USDC tier. Proration credits the remaining 15 days’ value from the old tier against the new one, yielding a precise adjustment.
Service deploys a smart contract that can withdraw tokens from users, enabling shared subscription logic across platforms.
This pull model, advocated in GitHub repositories on subscription designs, minimizes user friction while enabling granular calculations.
Essential Smart Contract Architecture for Proration
Begin with a Solidity contract managing states: active, expired, tier level, start/end timestamps. Use mappings for user data and events for invoicing transparency. Stablecoins like USDC anchor pricing against volatility, crucial as Ethereum fluctuates to $2,035.03 lows of $2,014.53 in 24 hours.
Key functions include subscribe(), upgradeTier(), and calculateProration(). The latter computes: (daysRemaining/totalDays) * priceDifference. Libraries like OpenZeppelin’s SafeMath prevent overflows in these computations.
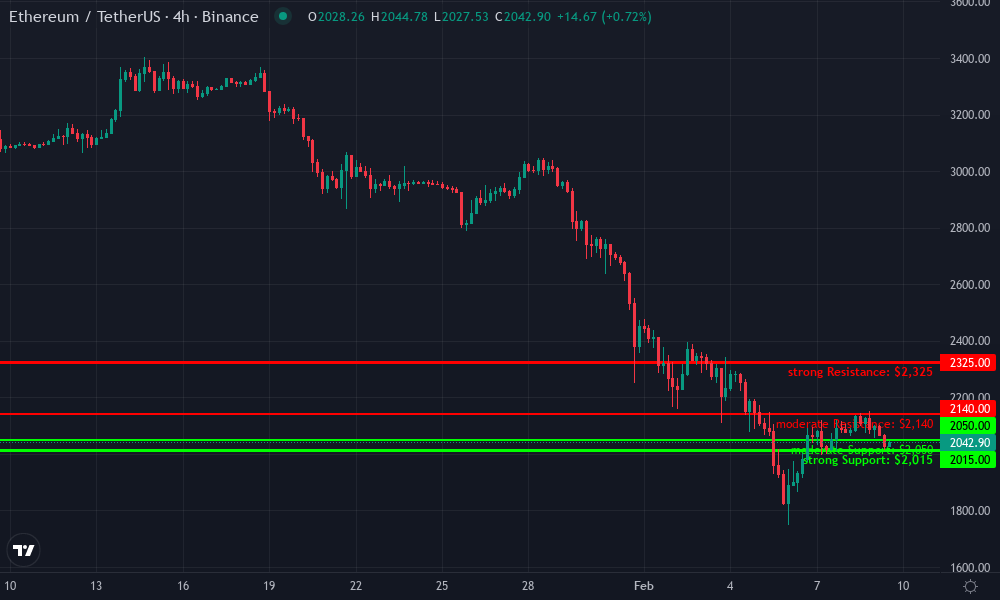
Integrate ERC-20 approvals for seamless pulls. For upgrades, the contract assesses time elapsed since last payment, refunds excess via prorated credits, then charges the delta. Downgrades work inversely, deferring credits to future cycles. This methodical logic, drawn from Medium guides on subscription contracts, ensures auditability. Deeper dives into proration implementation reveal how these contracts handle edge cases like leap years or irregular cycles. Pure onchain triggers falter under scale; enter Chainlink Automation. Register upkeep tasks to check expirations and execute prorations at cycle ends. This offchain oracle service calls your contract predictably, processing payments without user intervention. For finer granularity, Superfluid enables streaming payments. Subscriptions become continuous flows, where proration manifests as flow rate adjustments. Mid-cycle changes instantly recalibrate streams, ideal for usage-based SaaS. Pair with USDC for stability, as outlined in comprehensive guides to crypto billing flows. Consider a developer deploying on mainnet today. Gas fees, tied to Ethereum’s $2,035.03 price ecosystem, remain manageable. Test on Sepolia first: deploy, simulate upgrades, verify events log accurate prorations. Verification through events confirms the contract’s integrity before mainnet exposure. Emit detailed logs for proration deltas, tier shifts, and balances, enabling offchain dashboards to mirror onchain truth. This layered approach, rooted in Solidity best practices, fortifies ethereum subscription proration against exploits. Foundry or Hardhat streamline this process. Forge scripts simulate user journeys: subscribe mid-cycle, upgrade, assert prorated charges match expectations. For a 30-day cycle at 100 USDC basic to 150 USDC pro on day 10, expect (20/30)*50 USDC delta charged immediately. Precision here separates robust systems from brittle ones. Edge cases demand attention: partial days via block timestamps, timezone neutrality through UTC, leap seconds negligible onchain. Refunds via credits avoid dust transactions; defer to next cycle for sub-USDC amounts. These refinements elevate solidity prorated billing to production grade. Analysis by Graham Porter | Symbol: BINANCE:ETHUSDT | Interval: 4h | Drawings: 6 Graham Porter here, delivering a precise technical breakdown of this ETHUSDT daily chart spanning late February to early March 2026. The chart narrates a clear bearish story: a sharp rejection from the 2325 resistance zone mid-February, followed by a multi-day downtrend slicing through prior supports, now consolidating near the psychological 2000-2050 demand zone amid elevated volume on the selloff. Key drawing instructions in my style: 1. Sketch a prominent downtrend line (red, thick) connecting the swing high at 2325 on 2026-02-22 to the recent high at 2090 on 2026-03-07, extending forward—this channel defines the bearish bias. 2. Mark horizontal lines at key S/R: green at 2015 (strong support), yellow at 2050 (moderate), red at 2140 and 2325 (resistances). 3. Rectangle the distribution range from 2026-02-22 to 2026-03-04 between 2100-2320. 4. Add arrow_mark_down at the breakdown below 2150 on 2026-03-04. 5. Callout volume surge on down days post-2026-02-25 with ‘Bearish Volume Confirmation’. 6. Text note near current price: ‘Watch 2015 support for reversal signals’. 7. Long position marker at 2020 entry if bounce confirms. This setup screams caution but offers a disciplined swing long on support test. Analysis: Downtrend intact but nearing strong support amid 24h volatility (-4.15%); medium tolerance suits waiting for reversal signals rather than chasing Graham Porter’s Recommendation: Stand aside or scale into longs at 2020 on confirmation; preserve capital—charts reward patience. Pattern: Increasing on downside, confirming bearish momentum Volume spikes on red candles from 2026-02-25 to 2026-03-10, no bullish divergence yet Signal: Bearish crossover with momentum divergence potential MACD line below signal, histogram expanding negative; watch for hook up near lows This chart analysis utilizes the following professional drawing tools: Disclaimer: This technical analysis by Graham Porter is for educational purposes only and should not be considered as financial advice. Chainlink Automation shines for batch processing. Upkeeps poll subscriber mappings, executing renewals and prorations gas-efficiently. Budget LINK tokens accordingly; current setups handle thousands of users without faltering. For dynamic SaaS, Superfluid streams USDC flows, throttling access via sender balances. Proration? Adjust rates mid-stream, billing proportionally in real time. Consider compliance: KYC offchain if regulated, but onchain transparency logs all adjustments publicly. Pair with IPFS-hosted invoices for disputes. Guides from 0xProcessing underscore retries for failed transactions, vital as EVM lacks native persistence. SubscribeOnChain setup guides accelerate this, offering pre-audited templates for saas blockchain subscriptions. Deploy in minutes, customize proration params, integrate frontends via ethers. js. Platforms like this abstract complexities, letting developers focus on core value. SaaS operators gain revenue optimization: upsell mid-cycle without friction, retain via fair downgrades. Ethereum’s stability at $2,035.03, post its 24-hour low of $2,014.53, favors experimentation. Users appreciate immutable fairness; no more opaque prorations hidden in SaaS black boxes. Forward-thinking developers embed analytics: track churn via expired events, A/B test tiers through prorated cohorts. This data fuels iteration, turning subscriptions into growth engines. With tools converging, recurring payments ethereum proration transitions from niche to necessity for Web3 SaaS. Deploy today, harness blockchain’s audit trail for unparalleled trust. Your subscribers will notice the difference in every adjusted invoice. Automating Proration with Chainlink and Streaming Protocols
Step-by-Step Guide to Proration Implementation
Ethereum Technical Analysis Chart
Technical Analysis Summary
Risk Assessment: medium
Key Support & Resistance Levels
📈 Support Levels:
strong
moderate
📉 Resistance Levels:
moderate
strong
Trading Zones (medium risk tolerance)
🎯 Entry Zones:
medium risk
🚪 Exit Zones:
💰 profit target
🛡️ stop loss
Technical Indicators Analysis
📊 Volume Analysis:
📈 MACD Analysis:
Applied TradingView Drawing Utilities
Trading involves risk, and you should always do your own research before making investment decisions.
Past performance does not guarantee future results. The analysis reflects the author’s personal methodology and risk tolerance (medium).Scaling Proration for SaaS with Automation and Streaming
Method
Pros
Cons
Pull Payments
Deterministic, low gas
User approvals needed
Streaming (Superfluid)
Real-time proration
Higher complexity
Chainlink Automation
Hands-off renewals
External dependency